
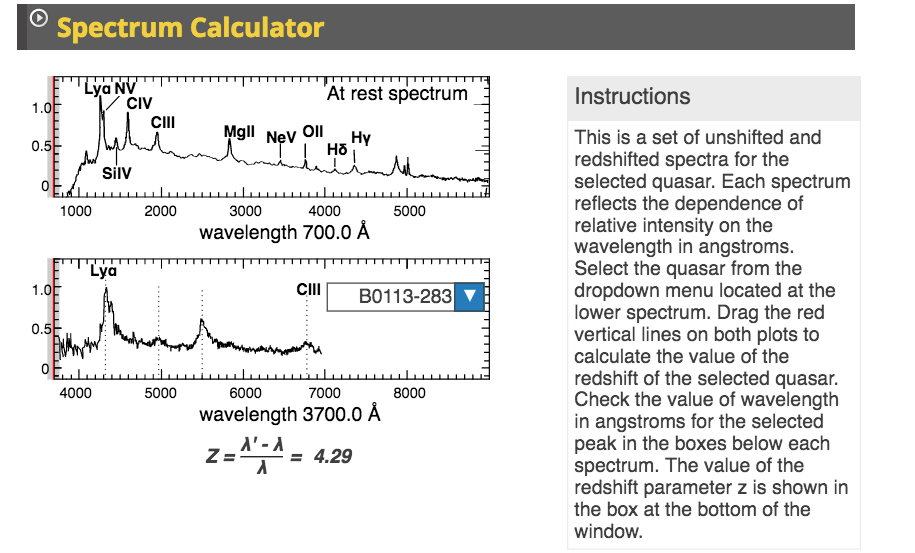
Z \equiv \frac$ is the observed frequency width or frequency difference. The redshift zis de ned z ob em em: (3) Substituting Equation 2 into Equation 3 we obtain z v c: (4) Note that the de nition is such that if vis positive, the source is moving away from the observer, and the wavelength of the light gets longer. Redshift is originally defined as the ratio of the difference between observed and emitted wavelength over emitted wavelength of electromagnetic radiation, hence As usual, I cannot guarantee that the information on this page is correct and accurate, so please be critical of what you read below.

There is no need to convert nanometres to metres as units cancel top and bottom.One this page I attempt to explain a few issues arising around the concept of redshift in astronomy. The equation quantifying this effect when. So if a distant galaxy emits a characteristic spectral line of 91 nm ( ultraviolet light at the 'Lyman limit') but when observed on Earth it appears to be 640 nm (red) we can calculate the red shift using this equation: We can use the shift to calculate how fast a light source, such as a star or galaxy, is moving towards us or away. The following equation is used to calculate redshift: What would it mean if your redshift were negative IV. Discussion question: You may have noticed that all your redshift figures are positive. Note: This equation only works for redshift smaller than z 1.0. with a being the scale factor, we can write. An example, if a supernova has a redshift of 0.025, then the radial velocity is given by. Starting with a definition of the Hubble parameter, H a a. Calculate the redshift of the galaxy using the following equation. This is because galaxies are receding (moving away) at such high speeds that relativistic effects need to be considered in calculations. I am trying to determine how an objects redshift (specifically, redshift due just to the expansion of the universe) changes in time. be expressed as zv/c (when v is much less than the speed of light), and v velocity. The Doppler equation used for sound calculations cannot be used in this situation. The Hubble parameter H is about 70 kilometers. Equation ( 7.226 ) defines 0 in terms of z ( implicitly ) equation. v cz Hd, where v is the recession velocity, z is the redshift, c is the speed of light, d is the distance. Redshift is also the name of the factor z indicating the relative change in wavelength due to the Doppler shift for a receding galaxy. the redshift by using the relation ( t / t ) 2/3 ( 1 + z ) ( 1 + z ) -1. In this theoretical framework, the observed redshifts zobs of distant galaxies map on to the scale factor through the standard formula 1 + zobs 1/a. The upper diagram shows the absorption spectrum from a stationary galaxy with one wavelength of light and no redshift. distance, which is a straight line at small distances, can tell us about the total amount of matter in the universe and may provide crucial information about the mysterious dark matter. In this way a plot of recession velocity (or redshift) vs. Lower diagram shows spectrum of light redshifted from a distant galaxy moving away from the Earth The amount of departure, and the type, depends on the value of the total mass of the universe. This indicated the stars were moving away from Earth (just as the sound of a siren moving away from you has a decreased frequency and increased wavelength).Īs the light was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum (lower frequency/longer wavelength) this phenomenon was termed 'redshift'. The same shifts in frequency and wavelength are also observed for light coming from stars in distant galaxies.īy comparing the light from distant stars with the spectrum of light from our Sun it was noticed that the spectra from distant stars had a slightly decreased frequency and slightly increased wavelength.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
